Skin redness can be caused by a variety of factors, including irritation, exposure to pollution, sun damage, (1) rosacea, (2) and eczema. (3) Those with sensitive skin are no strangers to this, but it is a problem that many people face on a regular basis.

You can try serums to reduce skin redness and to calm and balance your skin.
According to research done in 2019, an anti-redness serum that contains panthenol, palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), and niacinamide (NAM) reduces skin redness. (4)
Article Contents
Science-Backed Evidence That Serum Reduces Skin Redness
There is scientific proof that serum works to diminish redness. A 2019 study (4) provided information that an anti-redness (AR) serum dramatically reduced skin redness. No irritation, allergic reaction, or photoirritation was detected upon its use. Under typical usage circumstances, the serum was generally well tolerated.
The niacinamide, panthenol, and palmitoylethanolamide in the AR serum effectively helped reduce the facial redness brought on by winter xerosis in healthy volunteers with sensitive skin.
Additionally, anti-redness (AR) serum, which lacks UV filters, partially averts DNA deterioration. It also reduces redness by protecting the skin’s stratum corneum, or outer layer.
According to the researchers, redness can be reduced by using an AR serum containing glycerin, palmitoylethanolamide, niacinamide, and panthenol. (4)
Qualities of Ingredients in Anti-Redness Serums That Make It Helpful Against Skin Redness
Palmitoylethanolamide
It exhibits immunomodulatory, analgesic, antibacterial, and neuroprotective properties, (5) which contribute to a reduction in skin redness. (4)
Niacinamide
It has anti-inflammatory properties, enhances epidermal differentiation, improves skin moisture content, and reduces wrinkles, acne, and skin redness. (6)
Panthenol
It acts as a topical moisturizer and protectant. It is an anti-inflammatory and has been shown to improve epidermal differentiation (associated with several skin problems such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis), which lessens skin redness. (4)
Other ingredients used in AR serums that contribute to a reduction of skin redness are aqua, xylitol, isostearyl isostearate, pentylene glycol, hydroxyacetophenone, hydrogenated lecithin, acetamide MEA, palmitamide MEA, tocopheryl acetate, and sodium carbomer. (4)
Serums That Aid in Minimizing Skin Redness

The following serums can be effective in minimizing skin redness.
1. Serums rich in vitamins C and E
One of the naturally occurring antioxidants, vitamin C in serum form is in a nearly colorless state. (7) Vitamin C, one of the skin’s most potent antioxidants, has been demonstrated to defend against ultraviolet rays. (8)
Vitamin E works as a free-radical scavenger that protects the skin from a variety of harmful effects caused by sun radiation. (9) It also prevents the skin from becoming red. (10)
Vitamin C is the body’s primary source of vitamin E replenishment and works with it to protect cells from oxidative damage. According to researchers, serums containing vitamins C and E reduce skin redness. (11)
2. Serums high in polyphenols
The skin’s natural regeneration process is sped up by polyphenols, which play a role in stabilizing capillaries, improving microcirculation and skin elasticity, and protecting against damaging external elements such as UV radiation.
Polyphenols also relieve inflammation and reduce skin redness. (10) Polyphenols seem to work best at minimizing face erythema (redness of the skin). (12)
3. Serum BK46
Potassium alkyl glycinate (azelaic acid and glycerin combined), squalane, Aloe barbadensis (a houseplant) leaf juice, sodium hyaluronate, and other substances are included in Serum BK46. This serum also contains xanthan gum, which helps treat rosacea symptoms. (13)
Studies have found that applying Serum BK46 restored skin hydration and stopped water loss from the skin. Skin redness and erythema index were dramatically reduced with long-term Serum BK46 therapy. No side effects were observed, and Serum BK46 was perfectly tolerated.
Serum BK46’s moisturizing and skin barrier-restoring effects have been amply demonstrated in patients with mild to moderate rosacea. Thus, this product is an excellent choice for treating rosacea. (13)(14)
Home Remedies for Skin Redness
Here are some natural remedies that may help to reduce skin redness.
1. Homemade aloe vera serum
Aloe vera is frequently utilized for its antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties and has been studied extensively in medical science. It can help in retaining moisture and preserving skin integrity.
When applied to the face, aloe vera can help moisturize the skin. Using a small amount of aloe vera on the face regularly can help treat various skin conditions, including acne, eczema, and sunburn. Aloe vera also helps to reduce redness. (15)
How to apply:
- In a glass bowl, combine aloe vera gel from freshly cut aloe vera leaves and 2 tablespoons of organic rosewater.
- Break two vitamin E capsules into the mixture and thoroughly mix the ingredients.
- Fill a bottle with a dropper halfway with the mixture. Your face serum is now ready to use!
- Apply the serum to your face with your fingertips.
- Allow the serum to be absorbed into your skin without excessive rubbing.
2. Rub cucumber slices on the affected area
Cucumber is both an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory. Cucumber improves skin texture and treats skin conditions such as eczema and rosacea. It soothes skin inflammation and may aid in reducing redness. (16)
Cucumber slices can be applied directly to any red spots to cool, soothe, and reduce the redness.
3. Use ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is beneficial for various skin conditions because it has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial effects that soothe the skin, (17) improve its condition, and reduce redness.
How to apply:
- In a bowl, mix ½ teaspoon of ashwagandha powder with enough water to make a paste.
- Apply the paste to your face and neck and allow it to dry completely.
- Wash it off with cold water and pat your skin dry.
When to See a Doctor
If the redness on your face persists for more than 2 weeks, consult a dermatologist.
General Queries Related to Skin Redness
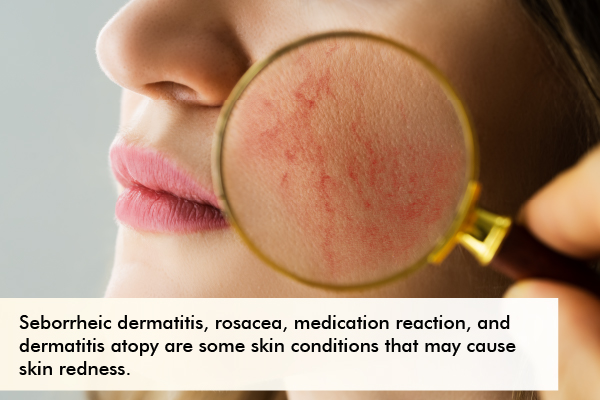
What are the skin conditions that may cause skin redness?
• Seborrheic dermatitis – It is a common skin condition that causes red rashes on the face.
• Rosacea – This skin condition is frequently preceded by a tendency to flush or blush easily. As the condition worsens, you may notice that the redness on your face lasts longer or never goes away.
• Medication reaction – When you spend time outside during the day, some medications can cause a sunburn-like reaction. Using medications, such as hydrocortisone (a steroid) creams, for longer than the recommended duration can also result in a skin reaction where redness of the skin develops.
• Dermatitis atopy – Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, can cause a rash with skin redness that appears suddenly. (18)
Does ice reduce skin redness?
Ice can be beneficial in reducing swelling, redness, and inflammation and also reduces the risk of scarring and post-inflammatory color change on the skin. Ice inhibits blood flow to the inflamed area and tightens the skin’s pores.
Final Word
Redness occurs in people with sensitive skin and also due to conditions such as erythema, rosacea, and eczema. People who are always exposed to the sun are prone to developing redness as well.
Applying an anti-redness serum containing glycerin, niacinamide, and panthenol helps to alleviate skin redness. Natural remedies can also be used to reduce skin redness. However, if the redness lasts longer than 2 weeks, consult a dermatologist.
References
- Erythema. Erythema – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/erythema.
- Pediatric alopecia areata following COVID‐19 infection. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jocd.15618.
- Eczema: Overview – informedhealth.org – NCBI bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279399/.
- Nisbet SJ, Targett D, Rawlings AV, et al. Clinical and in vitro evaluation of new anti-redness cosmetic products in subjects with winter xerosis and sensitive skin. International journal of cosmetic science. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6899962/. Published December 2019.
- Clayton P, Hill M, Bogoda N, Subah S, Venkatesh R. Palmitoylethanolamide: A natural compound for health management. International journal of molecular sciences. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8157570/. Published May 18, 2021.
- W; G. Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of cosmetic dermatology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17147561/.
- (PDF) vitamin C in dermatology – researchgate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237061438/.
- Al-Niaimi F, Chiang NYZ. Topical vitamin C and the skin: Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5605218/. Published July 2017.
- (PDF) vitamin E in dermatology – researchgate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305302250/.
- Michalak M, Pierzak M, Kręcisz B, Suliga E. Bioactive compounds for skin health: A Review. MDPI. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/1/203. Published January 12, 2021.
- N; LKGFS. A serum containing vitamins C & E and a matrix-repair tripeptide reduces facial signs of aging as evidenced by PRIMOS® analysis and frequently repeated auto-perception. Journal of cosmetic dermatology. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7756752/.
- Saric S; Clark AK; Sivamani RK; Lio PA; Lev-Tov HA; The role of polyphenols in rosacea treatment: A systematic review. Journal of alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28650692/.
- Maggioni D, Cimicata A, Praticò A, et al. A preliminary clinical evaluation of a topical product for reducing slight rosacea imperfections. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7183761/. Published April 21, 2020.
- Juhaščik M, Kováčik A, Huerta-Ángeles G. Recent advances of hyaluronan for skin delivery: From structure to fabrication strategies and applications. MDPI. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/14/22/4833. Published November 10, 2022.
- Hekmatpou D, Mehrabi F, Rahzani K, Aminiyan A. The effect of Aloe vera clinical trials on prevention and Healing of Skin Wound: A systematic review. Iranian journal of medical sciences. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6330525/. Published January 2019.
- (PDF) health beneficial effects of cucumber – researchgate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351580539/.
- Studies of ashwagandha (withania somnifera dunal) – researchgate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303343480/.
- 10 reasons your face is red. American Academy of Dermatology. https://www.aad.org/public/everyday-care/skin-care-secrets/face/facial-redness.







