Acids can be an excellent ingredient for your skin when used in the right concentrations. It is also important to choose the one that suits your skin needs.

Two such popular acids are mandelic acid and salicylic acid for the treatment of acne (1) and pigmentation. (2)(3) They also make the skin lighter, (4)(2) smoother, and younger (4)(5) and reduce the signs of aging. (4)(6)
Although they are both good for the skin, mandelic acid might be a better option for many people, as it can be used in high concentrations on all skin types, (7) including sensitive skin. (8)
Mandelic acid is gentler than salicylic acid and has no side effects. (4) It is ideal for people with sensitive and acne-prone skin and is suitable for all skin types.
Salicylic acid also has multiple advantages such as it can reduce acne scars, hyperpigmentation, and active acne, but mandelic acid is quite gentler. (1)
You can combine both to treat inflammatory acne and post-acne spots, but start with a low concentration.
Continue reading to learn more about mandelic acid and salicylic acid so you can choose what’s best suited for your skin based on your skin type and issues.
Article Contents
How Is Mandelic Acid Better Than Salicylic Acid?
According to experts, mandelic acid, similar to its fellow alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) lactic acid and glycolic acid, absorbs uniformly, slowly, and superficially into the skin due to its large particle sizes. It stays longer on the skin’s surface, making it suitable for all skin types. (7)
A 2019 research reported that a 45% mandelic acid peel (AHA obtained from the hydrolysis of bitter almond extract) is as effective as a 30% salicylic acid peel. Moreover, according to the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, mandelic acid alleviates the severity of mild to moderate facial acne vulgaris.
However, despite their effective similarities, 45% mandelic acid peel is considered better, more tolerable, and safer than 30% salicylic acid peel. (1)
According to researchers, mandelic acid is gentler and safer than salicylic acid, as it is the safest AHA agent and is suitable for all skin types, even in high concentrations. (7) Mandelic acid penetrates slowly and absorbs softly due to its large size, thus causing less irritation. (4)
Although there are no warnings on the use of mandelic acid or side effects, you should be cautious while stepping into the sun after applying it. Always wear an SPF 30 or higher sunscreen. The FDA issued that users using AHA-containing products, including mandelic acid, must consider the risks of UV exposure.
There is zero to minimal information on AHAs causing side effects such as skin irritation, flaking, and redness. (4) Salicylic acid may lead to peeling, dryness, scaling, redness, burning, or stinging on the application area, but it is rare to have a serious allergic reaction to this ingredient.
However, if serious allergic reaction symptoms occur, such as itching, rash, swelling (especially in the face, throat, or tongue), trouble breathing, and severe dizziness, consult your doctor immediately. (8)
Mandelic Acid Versus Salicylic Acid
Here is an overview of the key differences between mandelic acid and salicylic acid and what to choose for your skin type.

Mandelic acid
Mandelic acid is an AHA. It is referred to as almond acid, an aromatic alpha-hydroxycarboxylic acid obtained from the hydrolysis of bitter almond extract.
It is a raw material and a synthetic intermediate for preparing pharmaceutical compounds such as antibiotics.
Mandelic acid is a useful compound used in healthcare, chemical, skin care, and cosmetic industries. It has been used in skincare products for years to treat skin issues such as sun damage, acne, and photoaging. It treats irregular pigmentation and wrinkles effectively. (9)
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid’s name originates from salix (a Latin word), which means “willow tree.” It is a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA).
Salicylic acid has several health benefits; for instance, it serves as an ingredient in aspirin and has a therapeutic effect on skin conditions such as eczema and acne.
Moreover, it exfoliates the skin and facilitates the removal of dead skin cells. Thus, it is widely used in cosmetic products, (10) such as tonics, masks, creams, and shampoos.
Aside from its use in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, salicylic acid is also a raw material in the production of textiles and food.
What to use: Mandelic acid or salicylic acid?
Check the following pieces of scientific evidence on the use of mandelic acid and salicylic acid based on skin types and issues for you to make a better choice.
Skin type
According to experts, people with superficial acne and oily skin can use salicylic acid. Salicylic acid is applied topically in the treatment of scaling conditions such as dandruff, ichthyosis, and psoriasis.
If you have a sensitive and dry skin type, you can include salicylic acid in your skin care routine in moderation. Initially, you can use a 2% concentration and then increase it to 6%. (11)
According to the experts, mandelic acid, in high concentrations, is suitable for all skin types, (7) including dry, oily, (12) acne-prone, sensitive, and combination skin. (7)
Hyperpigmentation
A 2013 and 2015 research reported the effectiveness of mandelic acid in treating hyperpigmentation induced by acne scars. (13)(14) It can also treat post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). (14)
A 2019 research also reported the benefits of mandelic acid in enhancing skin pigmentation. (2)
According to experts, 30% salicylic acid effectively treats sun damage or melasma-induced hyperpigmentation. However, in dermatological practice, salicylate toxicity has been reported when 20% salicylic acid is applied to 50% of the body surface area, so it is advised to start with the least concentration. (3)
Increased melanin production leads to hyperpigmentation. (15)(16) Salicylic acid can treat post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) by stopping acne lesions from leaving dark marks and alleviating inflammation. (3)
Moreover, according to researchers, salicylic acid can reduce post-acne hyperpigmentation. (2)
Skin lightening
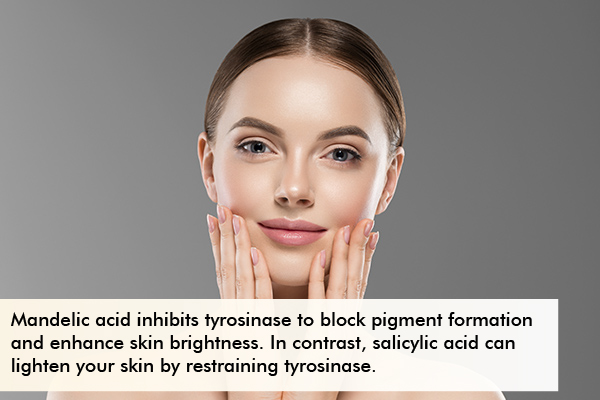
Experts say mandelic acid inhibits tyrosinase (a melanin-producing enzyme) and thus blocks pigment formation and enhances skin brightness.
A 2016 research reported that mandelic acid lightens darkly pigmented skin areas, such as sunspots, due to sun exposure, skin damage, and melasma (a skin condition that forms spots and patches that are darker than natural skin tone usually on the face). (17)(4) Thus, mandelic acid lightens the skin.
According to research, salicylic acid has whitening effects on the skin. (2) It can lighten your skin by restraining tyrosinase (16) (a melanin-producing enzyme). It prevents melanin transfer to other cells through the distribution of melanosomes, which are structures carrying melanin within melanocytes. (18)
Acne-prone skin treatment
Mandelic acid’s anti-inflammatory and comedolytic properties can reduce skin redness and swelling caused by inflammation and prevent whitehead and blackhead formation, respectively. (19)
Thus, mandelic acid is suitable for treating inflammatory acne, such as nodules, pustules, cysts, and pimples. Mandelic acid peel’s antibacterial property is beneficial for people with acne-prone skin. (4)
Experts also state that mandelic acid peel is safe, promising, inexpensive, and simple to use in the treatment of active acne that usually doesn’t respond to standard treatments. (20)
Salicylic acid is a BHA used in treating acne. (21) A 2016 research reported that salicylic acid is found in over-the-counter products for acne treatment. (22) Topical salicylic acid treats acne by reducing redness and swelling and unclogging obstructed pores for pimples to shrink. (23)
Improvement of appearance and skin aging
According to experts, the antiaging benefits of mandelic acid are similar to those of other AHAs, as they soften wrinkles and fine lines and enhance skin texture. (4)
A 2013 research reported mandelic acid’s effectiveness, safety, and tolerance in aging women by reducing the effects of the aging process, particularly regulating sebum secretion in areas where it has reduced considerably in dry skin. (24)
According to experts, salicylic acid improves skin aging signs and treats the signs of photoaging and intrinsic skin aging. The derivatives of salicylic acid reverse, treat, refine, and obstruct skin aging signs or enhance the aesthetic appearance of the skin. (6)
Mild exfoliation for smoother and younger skin
Mandelic acid elevates cell turnover, eliminating old and dull cells by dissolving the small bonds that hold skin cells together.
It swiftly discards dead skin cells from the skin surface to uncover healthy cells. This discarding rate makes the stratum corneum (outermost skin layer) thin. A thinner stratum corneum reflects the light better, making the skin look more youthful and smoother. (4)
Salicylic acid sheds dead skin cells from its outermost layer by increasing skin moisture content and dissolving the clumping of these cells. It makes removing skin cells easier, softening the skin’s top layer and reducing dryness and scaling.
Salicylic acid interacts with keratin (a skin protein). It gives rise to a complex formation that softens the skin’s outermost layer for easy shedding of dead skin cells at the superficial layer. (5) Its use results in youthful and smoother skin.
How to Use Mandelic Acid

Generally, mandelic acid can be used in the form of serum. Follow these steps to use a mandelic acid serum:
- Cleanse your face gently and pat it dry.
- Apply a skin toner and wait for 2–3 minutes.
- Using your fingertips, massage 2–3 drops of mandelic acid on your face for at least 5 minutes.
- Let it sit for at least 20 minutes.
- Apply a hydrating skin moisturizer.
You can also use mandelic acid as a cream or daily cleanser. You can also use it as a chemical peel once or twice weekly.
Note: As advised by experts, use mandelic acid in small amounts initially. Use it twice or thrice weekly and work your way up. (Few initial applications on the skin make it tolerant for everyday use). After cleansing and moisturizing, you can apply nighttime skin products containing mandelic acid.
How to Use Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid can be used in the form of gels, creams, pads, and plaster.
Follow these steps to use a salicylic acid gel, cream, or pad:
- Gently cleanse your skin to remove dirt and oils.
- Apply a wet pack or a thin layer to the affected area based on the product form (gel, cream, or pads).
- Use it once or twice daily or as suggested by your doctor.
Use a salicylic acid mask once or twice weekly for more thorough treatment for blemishes and spots. For peeling or exfoliation, use a high-concentration salicylic acid product (2%–6 %). (11)
Follow these steps to use a salicylic acid plaster:
- Cleanse your skin gently.
- Cut the plaster to size to fit the affected area (corn, wart, or callus).
- Place the plaster over the affected area and put a clean bandage or a band-aid over it.
- Repeat this based on your needs. For calluses and corns, use it every 48 hours for at least 14 days. For warts, use it every 48 hours.
Can Mandelic Acid and Salicylic Acid Be Used Together?
Some suggest mandelic acid and salicylic acid can be used together, and others suggest that doing so can cause damage to the skin.
However, recent research has shown that salicylic acid and mandelic acid peel together were effective in the treatment of inflammatory acne, noninflammatory acne, and post-acne hyperpigmentation. (25)
General Queries

Can you use salicylic acid during breastfeeding?
There is no clinical information if using salicylic acid on the skin during breastfeeding is recommended. Nevertheless, it is unlikely to get absorbed or appear in breast milk, so it is considered safe during breastfeeding.
However, avoid body areas that might come in contact with the infant’s skin or where the drug might get consumed by the infant via licking. (26)
Who should avoid using salicylic acid?
People with salicylic acid sensitivity, those with diabetes, infants, and those with impaired circulation should avoid its usage.
Additionally, avoid using it on birthmarks, moles, warts, ingrown hair, racial or genital warts, mucous membrane warts, and irritated, infected, or reddened skin areas. (11)
Final Word
Both salicylic acid and mandelic acid are chemical exfoliants that enhance the appearance of hyperpigmentation, wrinkles, acne, and more. But they are different in strengths and benefits based on skin sensitivity and acne type.
However, mandelic acid is better than salicylic acid as it is gentle and suitable for sensitive skin. Some people may use mandelic acid and salicylic acid together or alternately for best results.
References
- Log in to Wiley Online Library. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jocd.13168.
- Sarkar R, Ghunawat S, Garg VK. Comparative study of 35% glycolic acid, 20% salicylic-10% mandelic acid, and phytic acid combination peels in the treatment of active acne and Postacne Pigmentation. Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery. 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6785964/.
- Arif T. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: A comprehensive review. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology. August 26, 2015. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4554394/.
- RRJCES – Aelsindia.com. http://aelsindia.com/rjcesjune2016/6.pdf.
- An overview of Dandruff and novel formulations as a treatment strategy. Scribd. https://www.scribd.com/document/580834156/ArticleIJPSR2-Vol-9-Issue-2-Feb-2018-IJPSR-RE-2346.
- US20160193127A1 – cosmetic use of salicylic acid derivatives. Google Patents. https://patents.google.com/patent/US20160193127A1/en.
- Gentili G, Perugini P, Bugliaro S, D’Antonio C. Efficacy and safety of a new peeling formulated with a pool of phas for the treatment of all skin types, even sensitive. Journal of cosmetic dermatology. February 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10087944/.
- Rodan K, Fields K, Majewski G, Falla T. Skincare bootcamp: The evolving role of Skincare. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open. December 14, 2016. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5172479/.
- Separation of mandelic acid by a reactive extraction method using … https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363107914/.
- Synthesis of natural salicylic acid as a cosmetic ingredient using … https://www.researchgate.net/publication/359959757/.
- Salicylic acid. National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Salicylic-Acid#section=Information-Sources.
- Salicylic acid. National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database. https://www.jaad.org/article/S0190-9622(20)31574-7/fulltext.
- Wójcik A, Kubiak M, Rotsztejn H. Influence of Azelaic and mandelic acid peels on sebum secretion in ageing women. Postepy dermatologii i alergologii. June 2013. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3834725/.
- Dębowska RM, Kaszuba A, Michalak I, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and tolerability of mandelic acid-containing cosmetic formulations for Acne Skin Care. Dermatology Review/Przegląd Dermatologiczny. September 22, 2015. https://www.termedia.pl/Evaluation-of-the-efficacy-and-tolerability-of-mandelic-acid-containing-cosmetic-formulations-for-acne-skin-care,56,25608,1,1.html.
- Cestari TF, Dantas LP, Boza JC. Acquired hyperpigmentations. Anais brasileiros de dermatologia. 2014. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3938350/.
- Are tyrosinase inhibitors in sunscreens and … – Wiley Online Library. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/exd.12715.
- Melasma: Overview. American Academy of Dermatology. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/melasma-overview.
- EP0747043A1 – use of salicylic acid derivatives for skin whitening. Google Patents. https://patents.google.com/patent/EP0747043A1/en.
- Garofalo V, Cannizzaro MV, Mazzilli S, Bianchi L, Campione E. Clinical evidence on the efficacy and tolerability of a topical medical device containing benzoylperoxide 4%, retinol 0.5%, mandelic acid 1% and lactobionic acid 1% in the treatment of mild facial acne: An open label pilot study. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology. May 15, 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6526677/.
- Mandelic acid chemical peel in acne vulgaris: A Boon or a Bane? https://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jdms/papers/Vol14-issue5/Version-7/I014573235.pdf.
- Lu J; Cong T; Wen X; Li X; Du D; He G; Jiang X; Salicylic acid treats acne vulgaris by suppressing AMPK/SREBP1 pathway in sebocytes. Experimental dermatology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30972839/.
- Fox L, Csongradi C, Aucamp M, du Plessis J, Gerber M. Treatment modalities for acne. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). August 13, 2016. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6273829/.
- Salicylic acid topical: Medlineplus Drug Information. MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a607072.html.
- Wójcik A, Kubiak M, Rotsztejn H. Influence of Azelaic and mandelic acid peels on sebum secretion in ageing women. Postepy dermatologii i alergologii. June 2013. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3834725/.
- Andrology D of D and. Salicylic–mandelic acid versus glycolic acid peels in… : Journal of the Egyptian Women’s Dermatologic Society. LWW. https://journals.lww.com/jewds/Fulltext/2015/09000/Salicylic_mandelic_acid_versus_glycolic_acid_peels.10.aspx.
- Salicylic acid. National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Salicylic-Acid#section=Effects-During-Pregnancy-and-Lactation.