Both salicylic acid and retinol are excellent skin care ingredients for treating acne-prone, oily skin. However, the rumor is that these two don’t get along quite well.

So, the question is, can salicylic acid and retinol be used together?
Yes, you can use salicylic acid and retinol together. (1)(2) However, if you have sensitive or dry skin, mixing the two can cause skin irritation.
Note: Salicylic acid is used in acne treatment in 0.5%–5% concentration. (3) Retinol is used in concentrations between 0.0015% and 0.3%. (4)
Continue reading to learn more about using the salicylic acid and retinol cocktail.
Article Contents
Can Salicylic Acid and Retinol Be Used Together?
Yes, salicylic acid and retinol can be used together if there’s no skin irritation or your skin is sensitive; in such cases, it is not a great combination.
Both salicylic acid and retinol are effective skin care ingredients for treating acne-prone, oily skin (2) and offer excellent benefits. However, you must apply the two with caution.
A 2016 research showed that, when applied topically, retinol (all-trans-retinol) and salicylic acid improved acne vulgaris and photodamage and that they can be used daily. (1) A concentration of 0.25% retinol is safe and effective in reducing photoaging signs after salicylic acid peeling. (1)
Moreover, a 2019 research reported that topical application of retinol and salicylic acid with lactic acid resulted in acne improvement after 4 weeks, with continued progress after 8 weeks. (2)
Another research reported that acne treatment often included topical salicylic acid and retinol application. (5) Salicylic acid is a peeling agent that treats melasma, lentigines, freckles, photodamage, and acne vulgaris. (6)
Thus, salicylic acid and retinol can be used together.
What Are the Safe Dosages of Salicylic Acid and Retinol?
The safe dosages of salicylic acid and retinol are as follows.
Salicylic acid dosage
Salicylic acid is an odorless, white solid that plunges in and slowly mixes with water. (7) About 1%–2% of the total dosage of salicylic acid gets deposited on the skin at the time of washing. Researchers are looking for more effective deposition systems and more effective deposition systems are sought. (8)
The standard salicylic acid chemical peeling involves using 20% or 30% salicylic acid formulation in an ethanol base. (9) This study examines the effectiveness and safety of a 1.5% salicylic acid cream containing natural skin penetration enhancers and antioxidants for treating facial acne. (10)
Retinol dosage
Retinol in the form of liquid crystal is safe and has many clinical perks. (4)
Another study found that 0.25% retinol, 0.5% retinol, and 1.0% retinol were effective in improving visual skin smoothness and skin dryness and safe with better/equivalent tolerability and performance than tretinoin creams. (11)
What Is Salicylic Acid and What Are Its Properties?
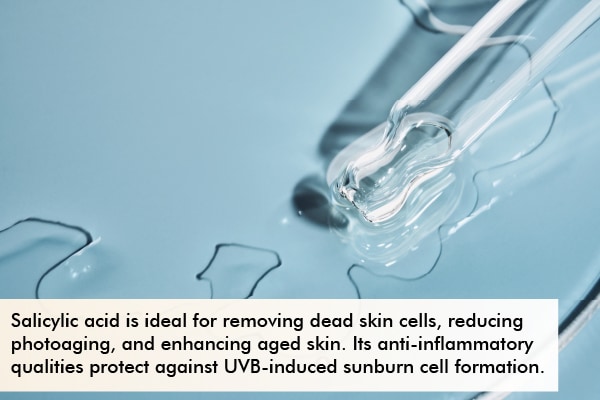
Salicylic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid. Its name stems from the Latin word salix, which means willow tree. The source of salicylic acid is white willow’s bark and wintergreen leaves. (7)
As an aspirin ingredient, salicylic acid has multiple health perks. It treats several skin conditions, such as eczema and acne. It is also used widely in numerous cosmetic products, (12) such as shampoos, creams, tonics, and masks. It also removes dead skin cells due to its exfoliating nature.
Moreover, salicylic acid is used in textiles, food, cosmeceuticals, and pharmaceuticals as a raw material.
The following are the properties of salicylic acid:
- It is ideal for removing dead skin cells, reducing photoaging, and improving aged skin. (13)
- It possesses anti-inflammatory properties that prevent sunburn cell formation due to exposure to UVB rays. (14)
- It shows mild to moderate activity against inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions. (15)
What Is Retinol and What Are Its Properties?
Retinol is vitamin A’s synthetic derivative. It is a fat-soluble vitamin found in foods such as dairy products, eggs, fish oil, and meat. (16)
Retinol boosts elastin and collagen production, which is essential for the smoothness and firmness of the skin. It reduces transepidermal water loss (TEWL), which refers to the amount of water evaporating from the skin surface. (4)
Retinal, retinol, retinoic acid, and other related compounds are referred to as retinoids.
The following are the properties of retinol:
- Retinol shows promising results in treating skin aging irritant reactions such as scaling and burning. (17)
- Retinoic acid enhances aged-looking skin. (18)
- All-trans retinol (retinoid acid’s precursor) is a widespread, effective antiaging agent used in skin care products. (19)
- Retinol improves fine wrinkles caused by natural aging. (20)
What Are the Adverse Effects of Salicylic Acid and Retinol?
Unfortunately, salicylic acid and retinol are not free of unpleasant effects.
The harmful effects of salicylic acid include:
- Toxicity to salicylate is a medical emergency.
- Intentional or accidental ingestion/overdose of salicylic acid can severely cause metabolic derangements, making treatment challenging.
- Levels of 100 mg/dL or more of salicylate are considered severely toxic, and the effects can be seen 12–24 hours after ingestion.
- Salicylic acid can damage the basement membranes of the body, leading to cerebral and pulmonary edema.
- In acute salicylic overdose, the symptoms usually occur within 3–8 hours, and the severity depends on the ingested amount. Mild ingestion (40 to 80 mg/dL) causes vomiting, nausea, and generalized abdominal pain. (21)
Note: According to one research, all congeners of salicylic acid showed potential antibacterial properties as they curbed the growth of different bacterial strains. (22) However, the results also showed the inactive nature of salicylic acid against various bacterial strains, including B. subtilis. (23)
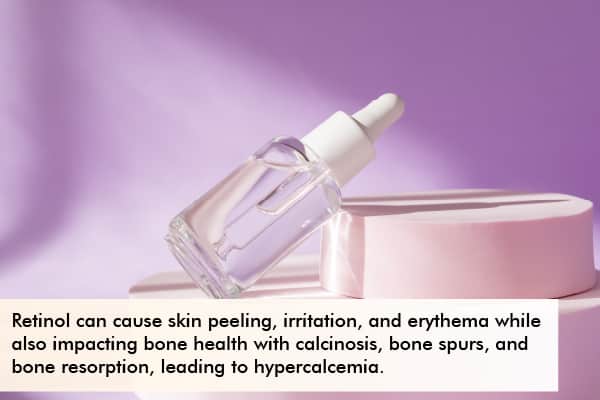
The harmful effects of retinol include:
- Skin peeling, irritation, and erythema are the most common retinol effects.
- Severe retinoid toxicity can affect several organs.
- Calcinosis, bone spurs, and bone resorption with hypercalcemia are retinol effects on bone health.
- Long-term dietary vitamin A consumption in high levels encourages bone resorption and stops bone formation, which can lead to hip fractures and osteoporosis.
- Other possible central nervous system effects are vomiting, nausea, and headache. (24)
General Queries
Can I use salicylic and retinol during pregnancy?
No studies have been done on the topical use of retinol and salicylic acid. However, if absorbed in small portions, they are unlikely to pose risks to a developing baby. (5)
Until a large-scale study is done, using retinol topically must be avoided due to its questionable risk benefits. (25) However, some theoretical considerations discourage the topical use of retinol and other topical acne products during pregnancy. (26)
Oral retinoid drugs are unsafe during pregnancy as they are linked to congenital malformations. (27) Phenol peels, trichloroacetic acid, and salicylic acid should not be used during pregnancy. (29)
If using retinol irritates the skin, how do I avoid it?
According to researchers, if you have sensitive skin, using retinol in high concentrations can lead to irritation. (29) They also suggest avoiding overly drying astringents and toners, as they can irritate the skin severely. (30)
According to some studies, genetic variations significantly affect retinoid and retinol’s bioavailability. Genetic factors govern retinol-induced irritation. (29)
How long after using salicylic acid can I use retinol?
Retinol in 0.25% concentration can be effectively and safely applied right after salicylic acid peeling to improve photoaging signs. (1)
It is recommended to stop using retinoids 1-2 weeks before peeling to prevent pre-peel complications. It should be discontinued days before the peeling procedure. (9)
Final Word
Salicylic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid with numerous health benefits and practical therapeutic effects on conditions such as acne and eczema. It also removes dead skin cells and is widespread in the cosmetic industry.
Retinol is a vitamin A derivative that boosts elastin and collagen production and thus enhances skin smoothness and firmness. It also reduces transepidermal water loss.
Using the amalgamation of salicylic acid and retinol is beneficial, but people with sensitive or dry skin should avoid this mixture.
References
- ZD; KD. Combination superficial peels with salicylic acid and Post-Peel retinoids. Journal of drugs in dermatology : JDD. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27050699/.
- Draelos Z;Lewis J;McHugh L;Pellegrino A;Popescu L; Novel retinoid ester in combination with salicylic acid for the treatment of acne. Journal of cosmetic dermatology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26516077/.
- Decker A, Graber EM. Over-the-counter acne treatments: A Review. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology. May 2012. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3366450/.
- Zasada M, Budzisz E. Retinoids: Active molecules influencing skin structure formation in cosmetic and dermatological treatments. Postepy dermatologii i alergologii. August 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6791161/.
- Bozzo P, Chua-Gocheco A, Einarson A. Safety of Skin Care Products during pregnancy. Canadian family physician Medecin de famille canadien. June 2011. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3114665/.
- T; A. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: A comprehensive review. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26347269.
- Salicylic acid. National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Salicylic-acid.
- MA; D. Salicylic acid deposition from wash-off products: Comparison of in vivo and porcine deposition models. International journal of cosmetic science. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25899428.
- Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: A comprehensive review – PMC. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4554394/.
- Zheng Y;Wan M;Chen H;Ye C;Zhao Y;Yi J;Xia Y;Lai W; Clinical evidence on the efficacy and safety of an antioxidant optimized 1.5% salicylic acid (SA) cream in the treatment of facial acne: An open, baseline-controlled clinical study. Skin research and technology : official journal of International Society for Bioengineering and the Skin (ISBS) [and] International Society for Digital Imaging of Skin (ISDIS) [and] International Society for Skin Imaging (ISSI). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23331850/.
- RS; DZ. A double-blind, comparative clinical study of newly formulated retinol serums vs tretinoin cream in escalating doses: A method for rapid retinization with minimized irritation. Journal of drugs in dermatology : JDD. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32574009/.
- (PDF) synthesis of natural salicylic acid as a cosmetic … – researchgate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/359959757/.
- Grajqevci-Kotori M, Kocinaj A. Exfoliative skin-peeling, benefits from this procedure and our experience. Medical archives (Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina). December 2015. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4720453/.
- D; MTDE. Salicylic acid protects the skin from UV damage. Journal of cosmetic science. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16758568/.
- Liu H, Yu H, Xia J, et al. Topical azelaic acid, salicylic acid, nicotinamide, sulphur, zinc and fruit acid (alpha-hydroxy acid) for acne. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. May 1, 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7193765.
- Vitamin A – statpearls – NCBI bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482362/.
- Mukherjee S, Date A, Patravale V, Korting HC, Roeder A, Weindl G. Retinoids in the treatment of Skin aging: An overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clinical interventions in aging. 2006. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2699641/.
- Shao Y, He T, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ, Quan T. Molecular basis of retinol anti-ageing properties in naturally aged human skin in vivo. International journal of cosmetic science. February 2017. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5136519/.
- Kong R;Cui Y;Fisher GJ;Wang X;Chen Y;Schneider LM;Majmudar G; A comparative study of the effects of retinol and retinoic acid on histological, molecular, and clinical properties of human skin. Journal of cosmetic dermatology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26578346/.
- Kafi R;Kwak HS;Schumacher WE;Cho S;Hanft VN;Hamilton TA;King AL;Neal JD;Varani J;Fisher GJ;Voorhees JJ;Kang S; Improvement of naturally aged skin with vitamin A (retinol). Archives of dermatology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17515510/.
- Salicylates toxicity – statpearls – NCBI bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499879/.
- Author links open overlay panelJyotirmaya Sahoo, Highlights•Synthesis of novel salicylic acid congeners.•Characterization by FT/IR, AbstractA series of azosalicylic acid analogs were newly synthesized by coupling various aryl and heteroarylamine functionalities with salicylic acid nucleus. All the synthesized compounds were structurally confirmed by various modern analytical methods. . Antimicrobial, analgesic, antioxidant and in silico study of synthesized salicylic acid congeners and their structural interpretation. Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. August 31, 2015. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2314808X15000603.
- Adamczak A, Ożarowski M, Karpiński TM. Antibacterial activity of some flavonoids and organic acids widely distributed in plants. Journal of clinical medicine. December 31, 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7019947/.
- Vitamin A toxicity – statpearls – NCBI bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532916/.
- Putra IB, Jusuf NK, Dewi NK. Skin changes and safety profile of topical products during pregnancy. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology. February 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8884185.
- Topical acne treatments – mother to baby | fact sheets – NCBI bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK582985/.
- Awan SZ, Lu J. Management of severe acne during pregnancy: A case report and review of the literature. International journal of women’s dermatology. July 13, 2017. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5555287/.
- C; B. [acne therapy in pregnancy]. Der Hautarzt; Zeitschrift fur Dermatologie, Venerologie, und verwandte Gebiete. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23430167/.
- Kang S, Kim K, Jun S-H, et al. Anti-irritant strategy against retinol based on the genetic analysis of Korean population: A genetically guided top-down approach. Pharmaceutics. November 25, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8706521/.
- Callender VD, Baldwin H, Cook-Bolden FE, Alexis AF, Stein Gold L, Guenin E. Effects of topical retinoids on acne and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in patients with skin of color: A clinical review and implications for Practice. American journal of clinical dermatology. January 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8776661/.